The Influence of Running in Place on Heart Rate
By: Brooke Buggia, Arafa Osman, Merita Mpawenayo, Ashylynn Urie, Tumaini
BIOL-202
Professor: Dr. Kabeer I. Ahammad sahib Ph.D.
Introduction
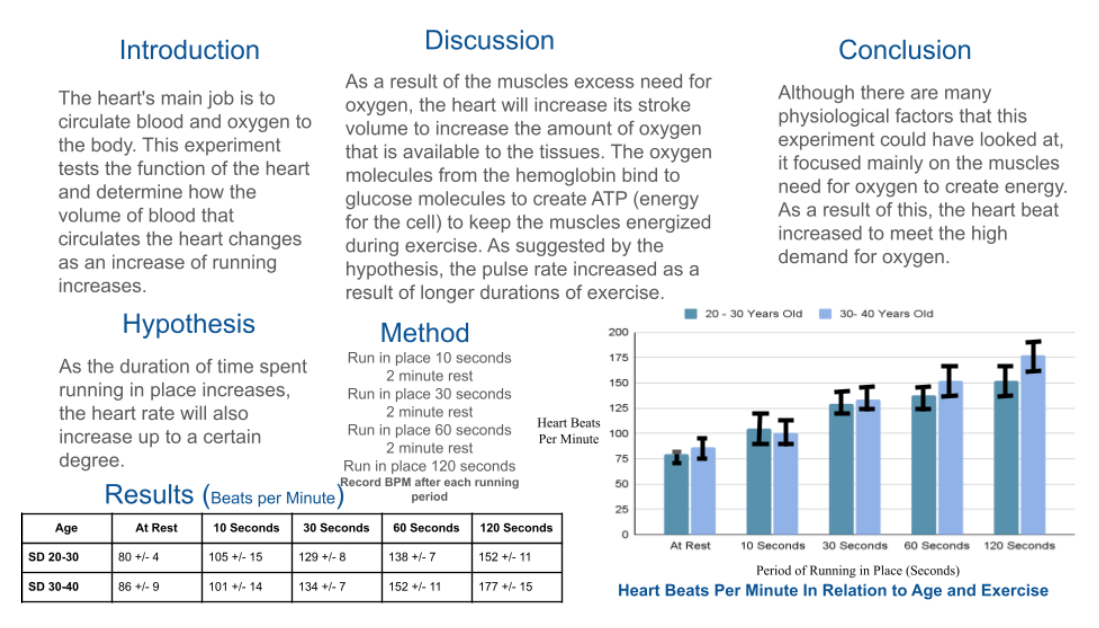
The heart’s main job is to circulate blood and oxygen to the body. This experiment tests the function of the heart and determine how the volume of blood that circulates the heart changes with an increase of running.
Hypothesis
As the duration of time spent running in place increases, the heart rate will also increase up to a certain degree.
Method to Recreate
- Run in place 10 seconds
- 2 minute rest
- Run in place 30 seconds
- 2 minute rest
- Run in place 60 seconds
- 2 minute rest
- Run in place 120 seconds
- Record BPM after each running period
Discussion
As a result of the muscles excess need for oxygen, the heart will increase its stroke volume to increase the amount of oxygen that is available to the tissues. The oxygen molecules from the hemoglobin bind to glucose molecules to create ATP (energy for the cell) to keep the muscles energized during exercise. As suggested by the hypothesis, the pulse rate increased as a result of longer durations of exercise.
Conclusion
Although there are many physiological factors that this experiment could have looked at, it focused mainly on the muscles need for oxygen to create energy. As a result of this, the heart beat increased to meet the high demand for oxygen.
References
Khan Academy. (2018). Cellular Respiration Review. Khan Academy; Khan Academy. https://www.khanacademy.org/science/high-school-biology/hs-energy-and-transport/hs-cellular-respiration/a/hs-cellular-respiration-review
NIH. (2022, March 24). How the Heart Works – How Blood Flows through the Heart | NHLBI, NIH. Www.nhlbi.nih.gov. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/heart/blood-flow#:~:text=The%20blood%20enters%20the%20heart